Fire Safety Managers (FSM) are generally the key personnel in preparing the evacuation process procedure to ensure all of the occupants can evacuate safely and systematically and prevent more damage to the properties or the casualties at the early stage of fire or emergency.
FSMs are responsible for developing, implementing, and maintaining fire safety procedures in buildings and ensuring that they are regularly tested and updated. They also conduct fire safety training for building occupants and work with fire safety organizations to respond to fire emergencies.
The Role of Fire Safety Manager
The role of an FSM is to ensure that fire safety regulations and standards are adhered to in buildings. This includes developing and implementing fire safety procedures, conducting fire risk assessments, and ensuring that fire safety equipment and systems are properly maintained and tested. FSMs are also responsible for providing fire safety training to building occupants and conducting regular fire drills to ensure that they are prepared for a fire emergency.
In addition to their day-to-day responsibilities, FSMs play a crucial role in responding to fire emergencies. They work closely with fire safety organizations such as the Fire and Rescue Department of Malaysia (Bomba Malaysia) to coordinate evacuation and rescue efforts and ensure that emergency responders have access to the building and necessary information.
The Importance of Fire Safety Managers in Malaysia
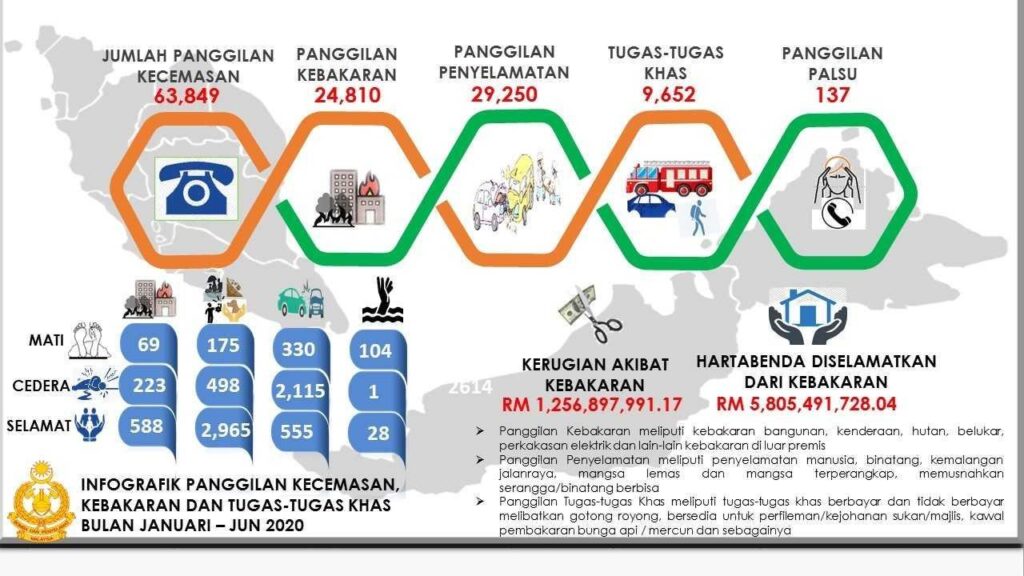
The importance of FSMs in Malaysia cannot be overstated. According to the Fire and Rescue Department of Malaysia, there were over 14,000 fire incidents reported in 2020 alone.
These incidents resulted in 139 deaths and over RM1.4 billion in property damage. Many of these incidents could have been prevented or mitigated with proper fire safety measures and procedures in place.
The government of Malaysia recognizes the importance of fire safety and has implemented various regulations and standards to ensure that buildings are safe from fire hazards.
The Uniform Building By-Laws 1984 (UBBL 1984) and Fire Services Act 1988 (FSA 1988) are two important pieces of legislation that outline the requirements for fire safety in buildings.
These regulations certified the appointment of an FSM in certain types of buildings, including high-rise buildings, hospitals, and shopping complexes.
In addition to regulatory requirements, the Fire Emergency Rescue Academy (FERA) provides guidance and resources to FSMs to help them fulfill their responsibilities.
FERA offers training courses and certification programs to ensure that FSMs are knowledgeable and up-to-date on the latest fire safety procedures and regulations.
Conclusion
FSMs responsibilities include developing and implementing fire safety procedures, conducting fire risk assessments, and providing fire safety training to building occupants. FSMs work closely with fire safety organizations to respond to fire emergencies and coordinate rescue efforts.
The government’s implementation of fire safety regulations and standards, along with the guidance and resources provided by organizations such as the FERA, have contributed significantly to improving fire safety in the country. It is crucial for buildings to appoint qualified and knowledgeable FSMs to prevent fire emergencies and protect lives and property.